

大豆植株有多种叶片形态,合适的叶形可提高光合效率,对产量和品质的提升具有重要作用。
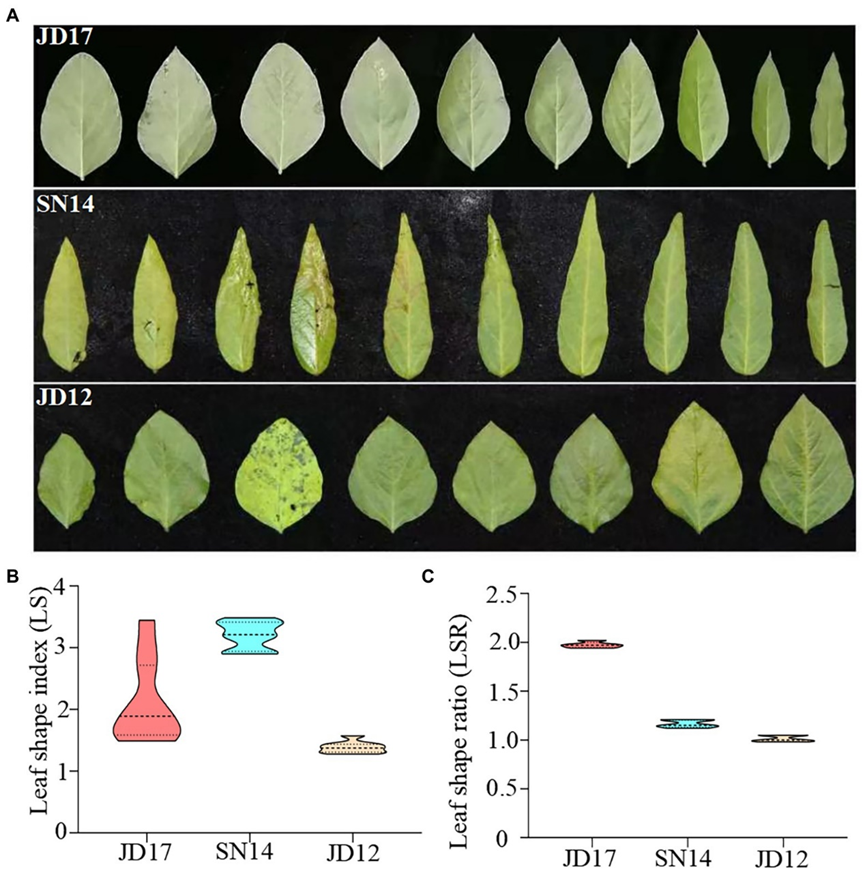
最近,河北省农林科学院张孟臣、杨春燕团队与澳大利亚CSIRO刘春吉博士等研究人员以异形叶大豆品种冀豆17、卵形叶品种冀豆12和披针形品种绥农14为亲本,构建了两个重组自交系(RIL)群体,用于识别在两个生长季中控制叶形的基因座。研究者在两个RIL群体中检测到8个生殖生长阶段的QTL,有4个可稳定遗传。其中,qRLS20在冀豆17x绥农14种群中影响最大,LOD值为46.9,这解释了高达47.2%的叶片表型变异率。该基因座与第20号染色体上的基部叶形QTL——qLSDOWN20位于同一基因组区域。另外,基因座qRLS19在冀豆17x冀豆12种群中影响最大,LOD值为15.2,表型变异为27.0%。该基因座与19号染色体上的顶端叶形QTL——qLSUP位于相同基因组区域。最后,根据两个RIL群体与三个亲本之间的序列差异、RT-qPCR分析和基因功能注释分析,研究人员确定了4个控制大豆叶形的候选基因:Glyma.01G151800、Glyma.18G279500、Glyma.19G194300和Glyma.20G116200。
该研究鉴定出大豆异形叶片QTL和候选基因,对大豆分子标记辅助育种及产量性状改良具有重要价值。
Front. Plant Sci., 16 Aug 2022
QTL and candidate genes for heterophylly in soybean based on two populations of recombinant inbred lines
Qiang Chen, Bingqiang Liu, Lijuan Ai …… Chunji Liu*, Chunyan Yang* and Mengchen Zhang*
*:Institute of Cereal and Oil Crops, Hebei Academy of Agricultural and Forestry Sciences, China;CSIRO Agriculture and Food, QLD, Australia
Heterophylly, the existence of different leaf shapes and sizes on the same plant, has been observed in many flowering plant species. Yet, the genetic characteristics and genetic basis of heterophylly in soybean remain unknown. Here, two populations of recombinant inbred lines (RILs) with distinctly different leaf shapes were used to identify loci controlling heterophylly in two environments. The ratio of apical leaf shape (LSUP) to basal leaf shape (LSDOWN) at the reproductive growth stage (RLS) was used as a parameter for classifying heterophylly. A total of eight QTL were detected for RLS between the two populations and four of them were stably identified in both environments. Among them, qRLS20 had the largest effect in the JS population, with a maximum LOD value of 46.9 explaining up to 47.2% of phenotypic variance. This locus was located in the same genomic region as the basal leaf shape QTL qLSDOWN20 on chromosome 20. The locus qRLS19 had the largest effect in the JJ population, with a maximum LOD value of 15.2 explaining up to 27.0% of phenotypic variance. This locus was located in the same genomic region as the apical leaf shape QTL qLSUP19 on chromosome 19. Four candidate genes for heterophylly were identified based on sequence differences among the three parents of the two mapping populations, RT-qPCR analysis, and gene functional annotation analysis. The QTL and candidate genes detected in this study lay a foundation for further understanding the genetic mechanism of heterophylly and are invaluable in marker-assisted breeding.

 首页 > 媒体报道
首页 > 媒体报道